
https://www.motherearthnews.com/organic-gardening/garden-transplanting-expert-advice-zmaz07amzsel
Tree planting has gotten extremely popular as the world explores for solutions to global climate change, with ambitious projects attempting to plant billions even trillions of trees. Other environmental aims are also included in these projects, such as controlling water cycles, preventing soil erosion, and restoring animal habitat. They frequently have socioeconomic objectives, such as poverty reduction. Let me you an in-depth insight of the process and the pre-requisites.
________________________________________________________________________
Read Also : When tree planting does more harm than good
________________________________________________________________________
Simple guide to Transplanting trees
A method of getting anything planted or relocated in your garden is by transplanting. Plants may be transplanted in two ways: by purchasing plants and transplanting them, or by moving plants from one location in your garden to another. These plants should not be allowed to mature in the containers in which they were purchased. You should either transplant them to the garden or into a larger container.
The crucial prerequisite for effective transplantation is that the exhalation of moisture from the leaves be maintained as low as possible while the roots are unable to offer their normal supply; as a result, deciduous trees can be transplanted safely after the leaves have fallen.
When the environment is dry and the sky is cloudless, moisture from the leaves of plants is exhaled most quickly; thus, if transplanting cannot be done in damp, cloudy weather, these circumstances should be ensured by shade and periodic spraying with water for plants in foliage.
All plants should be transplanted with a bulk of dirt over the roots if feasible. Lifting a ball of dirt with a plant that has huge woody roots and little fibrous roots near the stem, such as rose trees that have been growing in the same spot for several years, is ineffective. It should be gently dug out, with the roots as intact as possible, and transported to its new location, where the hole should be at least twice as large as the roots require. It is critical that the roots of the tree remain in their natural positions after being planted in the hole, and that they are not twisted or distorted in any manner.
Manure should never be applied directly to a plant’s roots; instead, fine soil should be applied first, followed by manure and soil. When transplanting trees, it’s a good idea to remove some of the smaller branches, especially any green buds that will perish otherwise. Exhalation through the stomata is reduced as a result, and the plant loses less moisture. Otherwise, the freshly planted tree will not be able to take root due to shifting winds.
The months of November and December are ideal for transplanting huge trees. It is not suggested to do this activity during the rainy season since it is difficult to maintain recently transplanted huge trees stable during that time. The hot season is also characterised by gales and is otherwise unpleasant.
If the tree to be transplanted is 6,0 6a circular trench, broad enough for the men to work in, must be dug two feet from the stem at the surface and gradually towards the centre as it descends, until the “ball” of dirt resembles an inverted cone. Thin planks 4 inches wide should be carefully assembled and secured to the sides of the ball of soil with ropes twisted to become very tight.
STEP TO STEP PROCEDURE OF TRANPLANTING
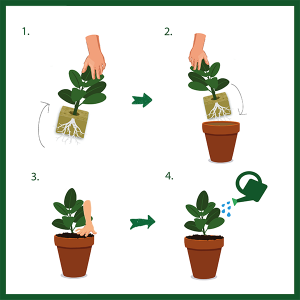
https://gardening.page/when-transplanting-a-plant/
- The essential procedures of transplanting are the same whether you’re reorganising your garden or starting with plants from a garden centre.
- Take the plant out of its container.
- Examine the roots. If the roots have fully covered the earth, gently pry them apart. If they’re clumped together at the bottom of the pot, loosen them up completely.
- Place the plant in a hole that has been prepared. If your soil is soft or sandy, the plant should be at or slightly above soil level.
- With your hands, compact the earth around the plant.
- There’s plenty of water. Watering the plant encourages its roots to grow deeper into the soil. It also aids the plant’s establishment in its new location.
________________________________________________________________________
Read Also : Planting trees “doesn’t make any sense” in the fight against climate change say experts
________________________________________________________________________
HOW TO TRANSPLANT AN OLD PLANT?

https://www.almanac.com/tips-transplanting-seedlings
In perennial garden plants, the monsoon season ushers in a new era of active development. It is an excellent time to repot old established plants when they emerge from their dormant phase. When the plant’s roots wrap around the inside of the pot, the plant is pot bound, and it’s time to move it to a larger container. Young and older plants require the same repotting procedures.
Pot pretreatment before repotting:
When repotting, a clean pot is vital. Pots that have become green due to past use should be soaked overnight in potassium permanganate and then washed. If you’re using fresh clay or earthen pots, soak them for 24 hours before using them. Plastic, ceramic, and metallic pots do not require any special care.
Repotting pot size:
Giving a plant a larger pot than it requires achieves nothing, since it causes waterlogging and drying off. Usually, a pot that is just a smidgeon bigger than the previous one would enough.
Taking the plant out of its previous pot:
The plant should be in dry soil so that it may be readily removed from its current container. One hand should be extended over the top of the dirt, holding the stem between the fingers, and then flip the pot to turn it out. If required, a root ball can be pushed into the drainage hole using a pencil to help it slip out. The drainage material must be removed, and the soil ball should be reduced using gentle pinching and rubbing motions until it is small enough to fit into a clean pot.
Plant repotting in a fresh pot:
- Drainage layers:
Between the cleaned ball of soil and the edge of the new pot, there should be 1 inch of room. By filling the hole at the bottom of the pot with a broken flower pot, curved side down, and then covering that with a bed of flower pot chips or gravel, enough drainage can be accomplished. Fine soil sliding through and obstructing drainage will be prevented by a covering of moss on top of this.
- Pruning damaged roots:
Use the sharpest knife you have to chop off any damaged roots. Roots can be pruned lightly if the plant is in an unusual form, and roots can be clipped back in moderation to encourage new development.
- Adding potting soil:
Place a little amount of moist potting soil in the container and gently pass it down. This new compost-rich soil should be tightly packed around the perimeter. The level of planting is indicated by the earth mark on the stem, and when the soil settles, the plant will sink to a little lower level.
________________________________________________________________________
Read Also : These 10 Golden Rules for Planting Trees Could Help Save the Planet
________________________________________________________________________
- Setting the dirt in the container:
Using a potting stick to move the soil down the edges of the pot is a good idea. The dirt should be evened out, and the plant should be well hydrated.
- Many garden plants generate offsets, suckers, rhizomes, and bulbs, which can be propagated during repotting. Simple division can be used to reproduce such plants when repotting. The plant should be carefully pushed apart after being knocked out of the container, since this frees the roots of excess soil. Plantlets are separated by stem/leaf/crown and removed with roots attached using a sharp knife. Each division is potted separately in a suitable sized container with a decent soil mix.







